Elements & Principles of ART
Introduction
Art elements are the basic units of any visual design which form its structure and convey visual messages.
The visual components of colour, form, line,shape, space, texture, and value.
Today we discuss on 'Line'
Line An element of art defined by a point moving in space. Line may be two-or three-dimensional, descriptive, implied, or abstract.
What is line ?
A line is defined as a one-dimensional entity having length but no breadth. In graphic design, it is metaphorically defined as ‘a line is a dot gone for a walk’, that is, a line is a point in motion.
A line can be thin or thick. It can have many variations in thinness and thickness.
Types of line
• Vertical lines
• Horizontal lines
• Diagonal lines
• Zigzag lines
• Curved lines
• Contour Line
Vertical Lines
In the visual arts, shape is a flat, enclosed area of an artwork created through lines, textures, colours or an area enclosed by
Lines that move up and down without any slant.
Instructions for students,
See the below image and find the other
example of vertical lines from their surrounding area
Horizontal Lines
Lines
that
are parallel to the horizon.
Instructions for students,
See the below image and find the other
example of horizontal lines from their surrounding area.
Diagonal Lines
lines
that slant.
Instructions for students,
See
the below image and find the other example of diagonal lines from their
surrounding area.
Zigzag Line
lines
made
from a combination of diagonal lines.
See the below image and find the other
example of zigzag lines from their surrounding area.
Curved Lines
Lines
that
change direction gradually
Instructions for students,
See the below image and find the other
example of Curved
lines from
their surrounding area.
Contour Line
A single line creating an outline of a figure or an object can show the height, width and even details of what is being studied. The word "contour" in art refers to an outline of the subject being studied.
Traditionally, it presents only the exterior edges of the object. A plain contour is one line that is connected with no shading, emphasizing the shell of the object.
Contour lines can suggest weight by pressing down harder or using the wider edge of a drawing instrument to create a thicker, denser line. To suggest that something is light or delicate, the line can
become thinner and lighter in color, using a pointed tip or pressing gently on the surface of the paper. A confident line can swiftly change dynamic of both bold and delicate within one gesture with a drawing instrument.
Blind Contour Line
Line drawings created without looking at the paper help to increase hand-eye coordination. A blind contour is best studied as a quick drawing while looking at either a figure or a still life. The line at first will seem very messy, however the more its practiced, hand-eye coordination will develop allowing for similarities in the actual object and the drawn object to relate more closely.
Many artists enjoy blind contour line drawings to help with freeing up the hand doing away with constraints of trying to get their drawings 'perfect'. Oftentimes, shapes or lines that are created during a blind contour study are whimsical and more interesting than what can be achieved from looking directly at the object.
Practice
• Drawing Straight Lines
• Let’s focus on drawing straight lines freehand, without a rular. Please note that the goal is to explore our abilities, and nothing more! We’re not trying to create “perfect” lines.
• If you feel unsure about drawing a straight line, I’d recommend outlining a line in pencil with a rular. This line should be barely visible as it will serve as a reference.
Note the repetition of uniform lines with a gradual variation in compositional devices of ‘orientation’ and ‘size’. These compositions with straight lines depict ‘movement and depth’.
Note the repetition of uniform lines with a gradual variation in compositional devices of ‘orientation’ and ‘size’. These compositions with straight lines depict ‘movement and depth’.
examples for practice👇🏻
Stay Home , Stay Happy, Stay Safe
Today’s Exercise
• Create a picture with lines only (Choose type
of any one category- means if you start with
horizontal lines than you must draw whole
picuter with same style of lines but you can
change thickness and length of line.
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA No1, Shahibaug
Jaswant Charan
Mob. - 8005730919
Email -arteducation95@gmail.com
Full video of this lesson
2.
Today we discuss on‘Shape’
In the visual arts, shape is a flat, enclosed area of an artwork created through lines, textures, colours or an area enclosed by
other shapes such as triangles, circles, and
squares.
What is Shape ?
Shape as a Visual Element of Art. The Visual Element of Shape can be natural or man-made, regular or irregular, flat (2-dimensional), representational or abstract, geometric or organic, transparent or opaque, positive or negative, decorative or symbolic, colored, patterned or textured.
Shape An element of art that is two-dimensional, flat, or limited to height and width
Types of shape
A shape is a defined 2-dimensional area.
The two types of shapes are geometric and free-form, which differ in the contours they are characterized by. Geometric shapes are classified by name like circle, square, rectangle, and triangle. Free-from shapes are generally irregular, uneven, and often found in nature.
Geometrical shape
IMPORTANCE OF SHAPE
Shapes can play important roles in the creation of art. They help to create complex drawings and paintings, affect composition, and contribute to the balance within a
work. Shape is a two-dimensional area that is defined by a change in value or some other form of contrast.
Today’s Exercise
Create a picture with shape/shapes only
(Choose any one shape- means if you start with shape-circle than you must complete whole drawing with same shape – circle
Or You use multi / different shapes
This lesson's video
This lesson's video
3. Now we learn about ‘Form’
Form as an element of art is three-dimensional and encloses space. Like a shape, a form has length and width, but it also has depth. Forms are either geometric or free-form.
As an Element of Art, form connotes something that is three-dimensional and encloses volume, having length, width, and height, versus shape, which is two-dimensional, or flat. A form is a shape in three dimensions, and, like shapes, can be geometric or organic.
As an Element of Art, form connotes something that is three-dimensional and encloses volume, having length, width, and height, versus shape, which is two-dimensional, or flat. A form is a shape in three dimensions, and, like shapes, can be geometric or organic.
“Form” and “shape” define objects situated in space. The basic difference, though, between “shape” and “form” is that “form” is in 3D while “shape” is plain 2D. The latter is simply defined by lines. When you see typical art drawn on simple drawing, printing, or painting surface, you immediately see shapes.
Different types of form
Shapes are the most basic figures like rectangles, circles, triangles, and squares while forms are the more complex structures like sphere, cube, cone, pyramid, prism, cuboid, etc.
Shapes are in 2D (have length and width) while forms are in 3D (have length, width, and height).
Importance of form
As one of the elements of art, along with the line, shape, texture, value, space, and color, form in art helps artists to produce an illusion of 3D and depth on a two-dimensional surface.
In a broader sense, form in art means the whole of a piece's visible elements and the way those elements are united. In this context, form allows us to mentally capture the work and understand it.
Observe and study the following references
By using single type of form-pyramid , create a design.
By using single type of form-sphere , create a design.
By using single type of form-sphere , create a design.
By using different types of geometrical form , create a picture.
By using different types of form , create a design.
By using forms , create your own design.
4.Now we learn about - Colour
colour means-
Colour is present when light strikes an
object and it is reflected back into the eye, a reaction to a hue arising in
the optic nerve. The first of the properties is hue, which is the
distinguishable colour, like red, blue or yellow. The next
property is value, meaning the lightness or darkness of the hue.
Colour has three main characteristics: hue (red, green, blue, etc.), value (how light or dark it is), and intensity (how bright or dull it is). Colours can be described as warm (red, yellow) or cool (blue, gray), depending on which end of the colour spectrum they fall. Value describes the brightness of colour.
Hue is another name for the word colour. Hue is one of the three properties of colour.
The word colour is the general term which applies to the whole subject - red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, black and white and all possible combinations thereof. Hue is the correct word to use to refer to just the pure spectrum colours. Any given colour can be described in terms of its value and hue.
Types of Colour:
There are three different types of colors: primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. The primary colors are red, yellow, and blue. The secondary colors are green, orange, and purple. And the tertiary colors are yellow-orange, red-orange, red-purple, blue-purple, blue-green, and yellow-green.
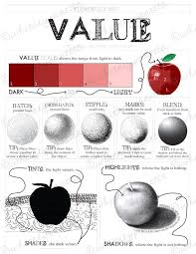
5.Now we learn about ‘Value’
Value in art is
essentially how light or dark something is on a scale of white to black (with
white being the highest value and black being the lowest value). It
is widely considered to be one of the most important variables to the success
of a painting, even more so than your selection of color (hue).
IMPORTANCE OF VALUE
Value deals with the lightness or
darkness of a color. Since we see objects and understand objects because of how
dark or light they are, value is incredible important to art. ... Value is the
key to the illusion of light. This is why value is so incredibly important to
drawing and painting.
6.Now we learn about ‘Space’
Space, as one of the classic seven elements
of art,
refers to the distances or areas around, between, and within components of a
piece. Space can be positive or negative, open
or closed, shallow or deep, and two-dimensional or three-dimensional.
Types of Space
There are two types of space that
exist within art — positive space and negative space. Positive space is the
actual objects or shapes within an artwork and negative space is the space
around and between those objects.
Space in a work of art refers to a
feeling of depth or three dimensions. It can also refer to the artist's use of
the area within the picture plane. The area around the primary objects in a
work of art is known as negative space, while the space occupied
by the primary objects is known as positive space.
IMPORTANCE OF SPACE
The Element of Design Space refers
to the area within, around, above or below an object or objects. It is important to
creating and understanding both two dimensional or three dimensional works
of art. ...
Two dimensional artists use a number of "tricks" for creating the
illusion of depth in their art.
Shapes can play important roles in the
creation of art. They help to create complex drawings and paintings, affect
composition, and contribute to the balance within a work. Shape is a
two-dimensional area that is defined by a change in value or some other form of
contrast.
Study the images and create your own work
with negative/ positive space.
7.Now we learn about ‘Texture’
In the visual arts, texture is the
perceived surface quality of a work of art. It is an element of two-dimensional
and three-dimensional designs and is distinguished by its perceived visual and
physical properties. Use of texture, along with other elements of design, can
convey a variety of messages and emotions.
In the visual arts, texture is
the perceived surface quality of a work of art. It is an element of
two-dimensional and three-dimensional designs and is distinguished by its
perceived visual and physical properties. Use of texture,
along with other elements of design, can convey a variety of messages and
emotions.
Texture is
the way something feels to the touch, or looks to the eye. Words like rough,
silky, shiny and dull help writers describe the texture of
an object. An artist shows texture to
accomplish the same goal. There are two types of texture:
tactile and visual.
................................................................................................
There are two types of texture:
tactile and visual.
Textures can
be described as “rough”, “smooth”, “hard”, “soft”, “liquid”, “solid”, “lumpy”,
“gritty” etc. The word “texture” is used for any different things.
It can even be used in abstract senses, e.g. for music and poetry.
The texture stimulates
two different senses:
sight and touch. There are four types of texture in
art: actual, simulated, abstract, and invented texture.
Texture
is the
character of a surface and is both tactile and visual.
Tactile
texture is the tactile quality of a surface, such as rough, smooth,
sticky, fuzzy, soft or slick. A real texture is one you can actually feel
with your hand, such as a piece of sandpaper, a wet glass, or animal fur. It
also can be created by an artist by doing a collage.
Tactile texture is the real thing. It is the
actual way a surface feels when it is felt or touched, such as rough, smooth,
soft, hard, silky, slimy, sticky, etc. 3-D art such as sculpture and
architectural structures are tactile in nature because they can be felt.
...................................................................................................................
Visual texture is the real thing. Real
texture cannot be represented here because a computer screen, even with the
highest quality photographs
can
only create simulate textures. However for the purpose of providing
examples
assume that these images are real.
Today’s Exercise
1.Draw small size of rectangles on a
sheet, and create different types of texture. (you may use any medium- eg
pencil, pen, colour, sketh-pen etc.)
2.Close your eyes and touch different
type of surface and feel it’s texture.
NAVIN K AMIN
TGT-ART EDUCATION
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA No.1, GANDHINAGAR
9428049878




























































good start....
ReplyDeleteThankyou sir
ReplyDelete